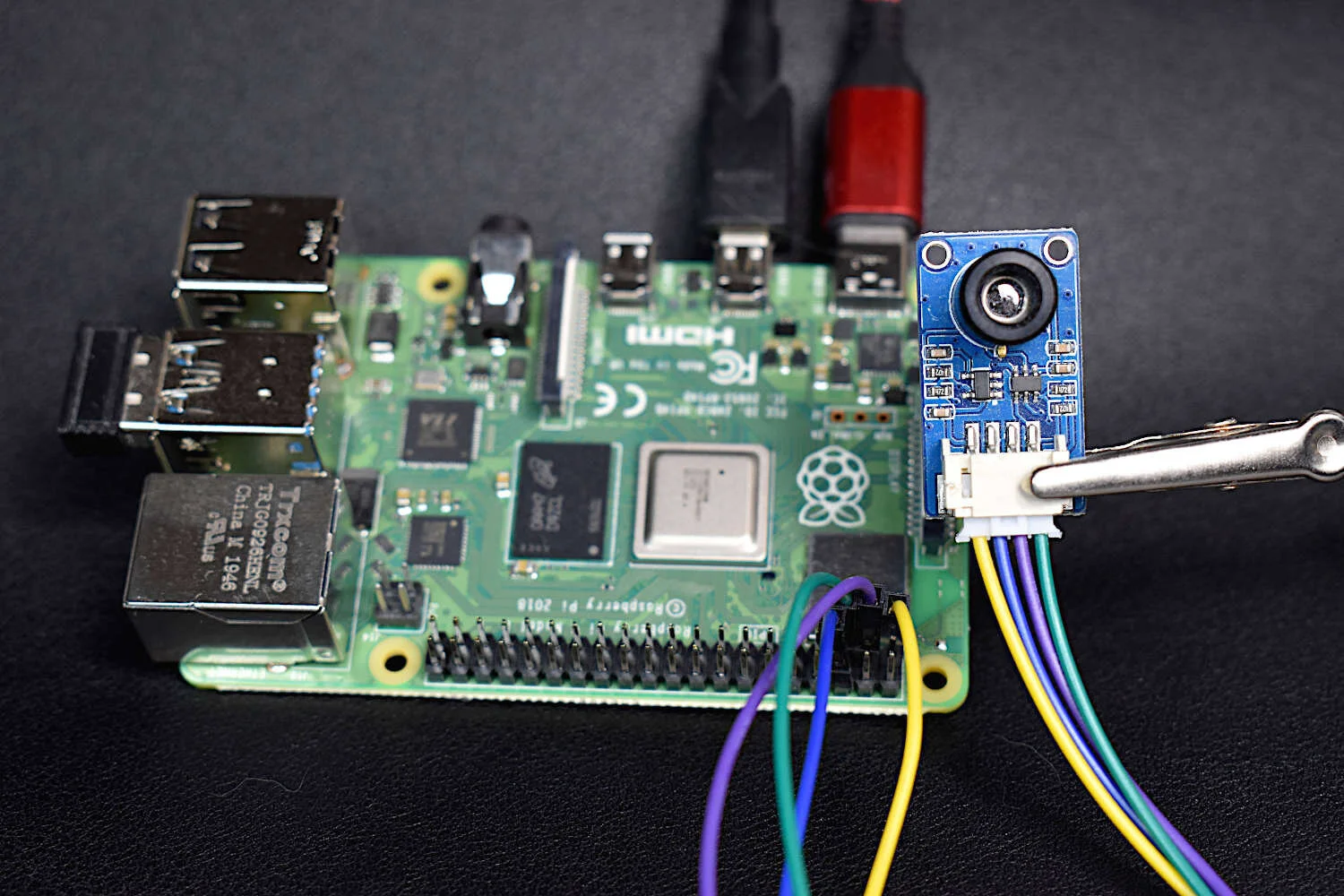
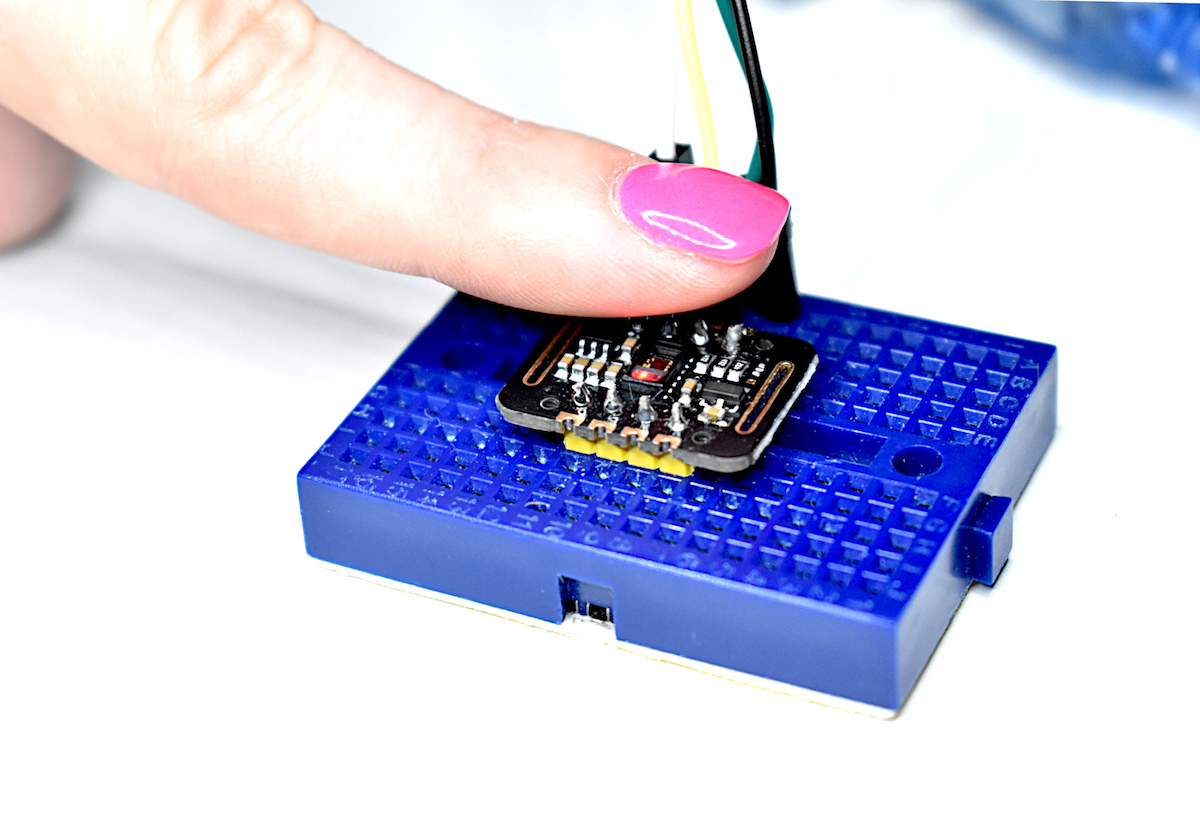
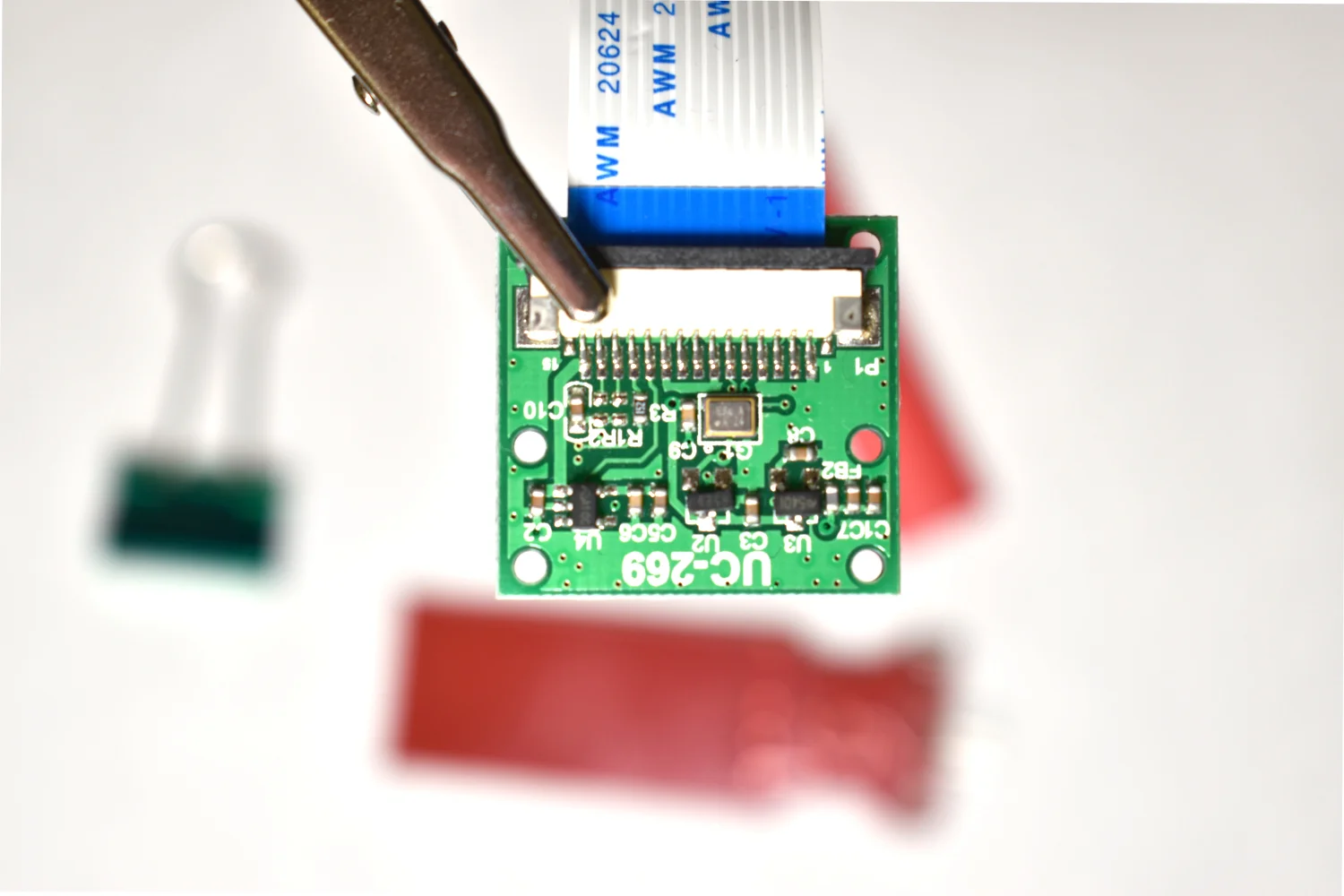
Thermal cameras are similar to standard cameras in that they use light to record images. The most significant distinction is that thermal cameras detect and filter light such that only the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum is recorded, not the visible region [read more about infrared cameras here]. Shortly after the discovery of the relationship between radiation and the heat given off by black bodies, infrared detectors were patented as a way to predict temperature via non-contact instrumentation. In recent decades, as integrated circuits shrink in size, infrared detectors have become commonplace in applications of non-destructive testing, medical device technology, and motion detection of heated bodies. The sensor used here is the MLX90640 [datasheet], which is a 768 pixel (24x32) thermal camera. It uses an array of infrared detectors (and likely filters) to detect the radiation given off by objects. Along with a Raspberry Pi computer, the MLX90640 will be used to map and record fairly high-resolution temeperature maps. Using Python, we will be able to push the RPI to its limits by interpolating the MLX90640 to create a 3 frame-per-second (fps) thermal camera at 240x320 pixel resolution.
Read MorePython’s file transfer protocol (FTP) library is used to parse weather station data from the publicly available automated surface observing system (ASOS) from the U.S.A.’s National Climatic Data Center (NCDC). Several programmatic tools available in Python are used to automate the parsing of weather data, as well as visualizing the resulting data.
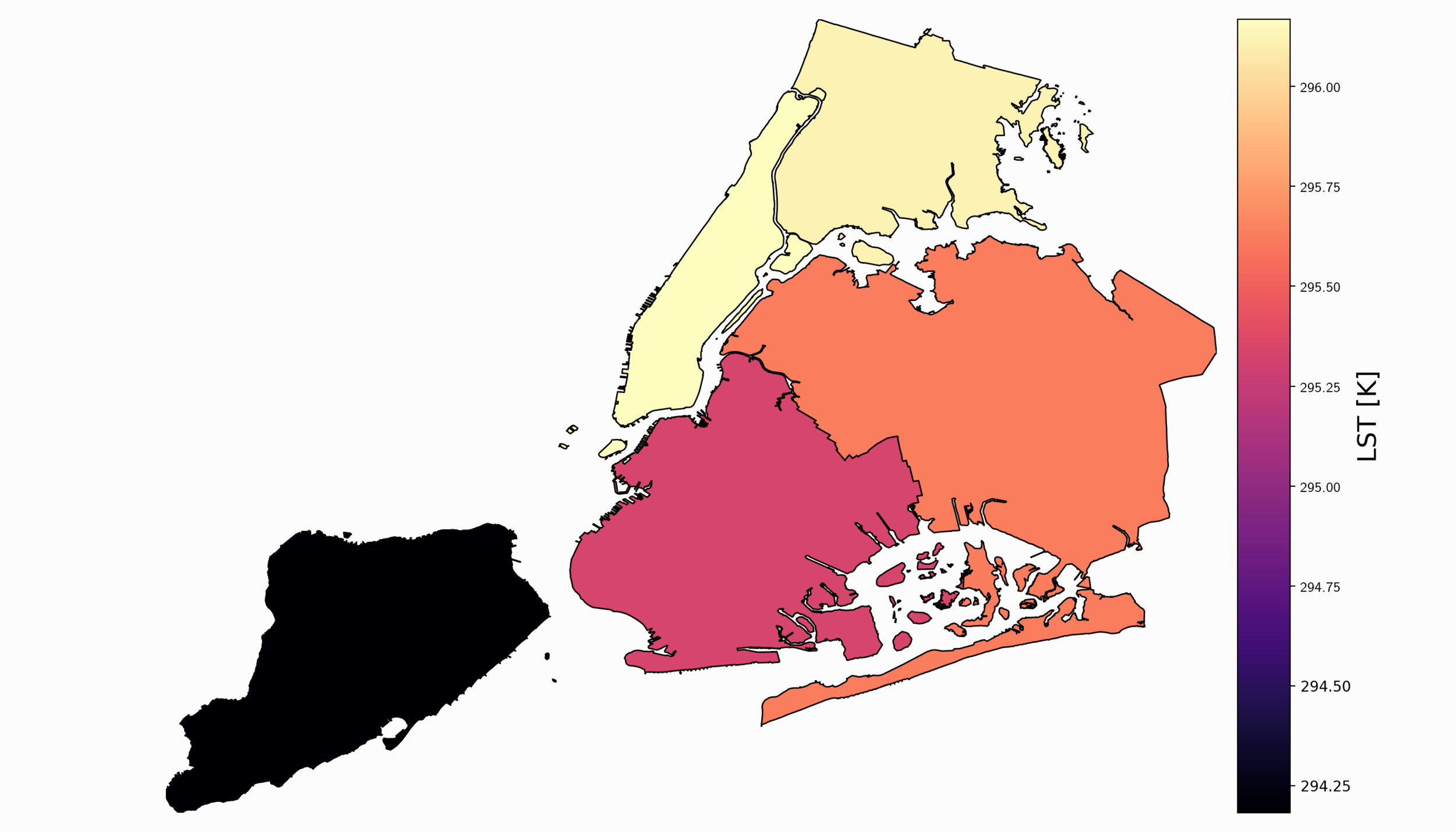
Read MoreFor part II, the focus shifts from the introduction of file formats and libraries to the geospatial analysis of satellite images. Python will again be used, along with many of its libraries. Land Surface Temperature will again be used as the data information, along with shapefiles used for geometric boundary setting, as well as information about buildings and land cover produced by local governments - all of which are used in meteorological and weather research and analyses.
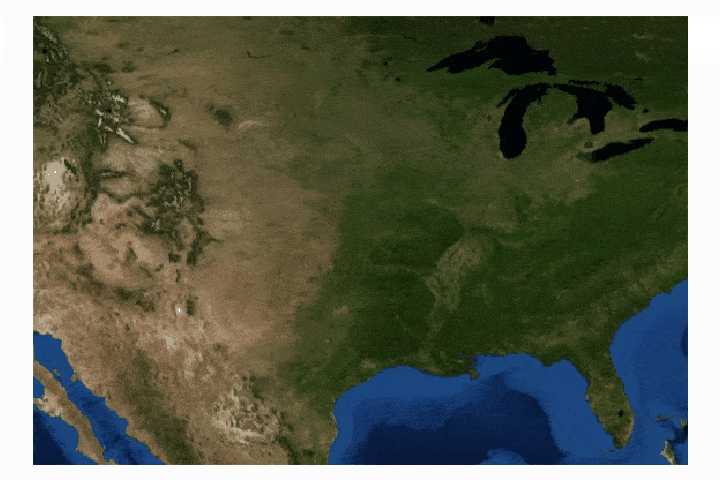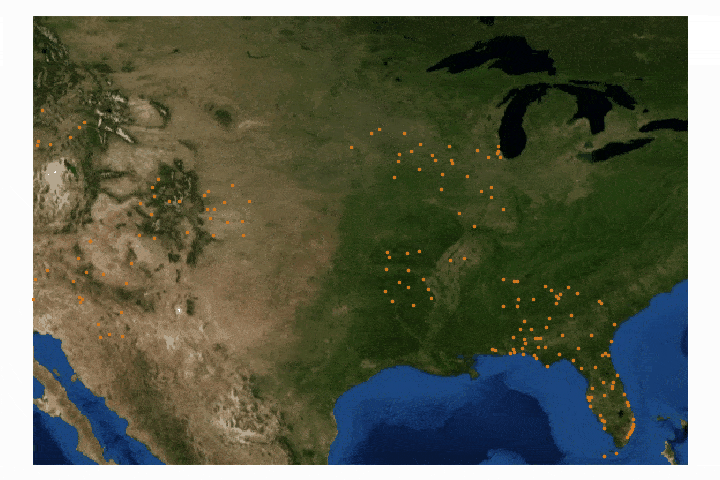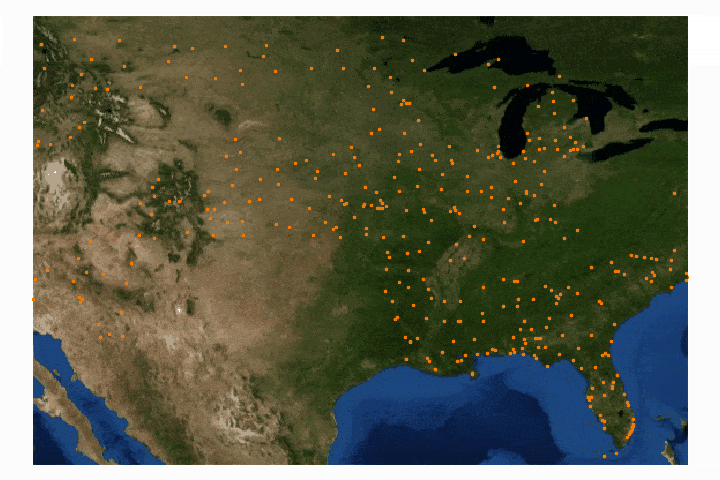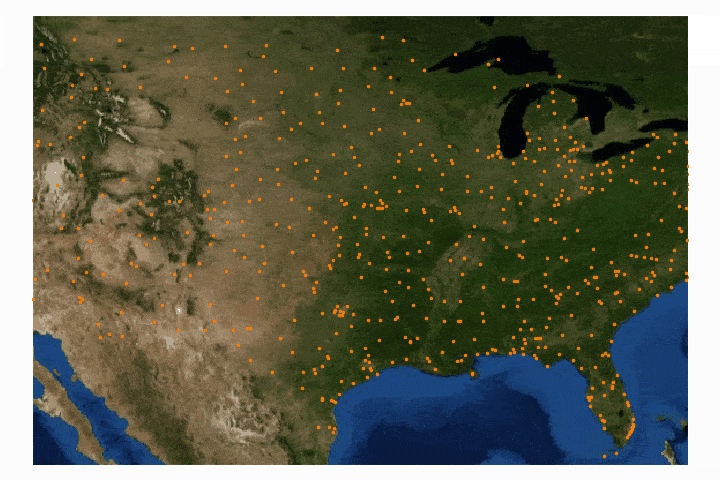
Read MoreIn this tutorial series, Python’s Basemap toolkit and several other libraries are utilized to explore the publicly-available Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-16 (GOES-16). In this first entry, the following will be introduced: acquisition of satellite data, understanding of satellite data files, mapping of geographic information in Python, and plotting satellite land surface temperature (LST) on a map.
Read MorePulse oximetry monitors the oxygen saturation in blood by measuring the magnitude of reflected red and infrared light [read more about pulse oximetry here and here]. Pulse oximeteters can also approximate heart rate by analyzing the time series response of the reflected red and infrared light . The MAX30102 pulse oximeter is an Arduino-compatible and inexpensive sensor that permits calculation of heart rate using the method described above. In this tutorial, the MAX30102 sensor will be introduced along with several in-depth analyses of the red and infrared reflection data that will be used to calculate parameters such as heart rate and oxygen saturation in blood.
Read MoreThe picamera and edge detection routines will be used to identify individual objects, predict each object’s color, and approximate each object’s orientation (rotation). By the end of the tutorial, the user will be capable of dividing an image into multiple objects, determining the rotation of the object, and drawing a box around the subsequent object.
Read MoreIn this entry, image processing-specific Python toolboxes are explored and applied to object detection to create algorithms that identify multiple objects and approximate their location in the frame using the picamera and Raspberry Pi. The methods used in this tutorial cover edge detection algorithms as well as some simple machine learning algorithms that allow us to identify individual objects in a frame.
Read MoreThe Raspberry Pi has a dedicated camera input port that allows users to record HD video and high-resolution photos. Using Python and specific libraries written for the Pi, users can create tools that take photos and video, and analyze them in real-time or save them for later processing. In this tutorial, I will use the 5MP picamera v1.3 to take photos and analyze them with Python and an Pi Zero W. This creates a self-contained system that could work as an item identification tool, security system, or other image processing application. The goal is to establish the basics of recording video and images onto the Pi, and using Python and statistics to analyze those images.
Read MoreTime of flight (ToF) is an approximation of the time it takes a traveling wave to come in contact with a surface and reflect back to the source. Time of flight has applications in automotive obstacle detection, resolving geographic surface composition, and computer vision and human gesture recognition. In the application here, the VL53L1X ToF sensor will be used to track the displacement of a ping pong ball falling down a tube. We can predict the acceleration and behavior of a falling ping pong ball by balancing the forces acting on the ball, and ultimately compare the theory to the actual displacement tracked by the time of flight sensor.
Read More