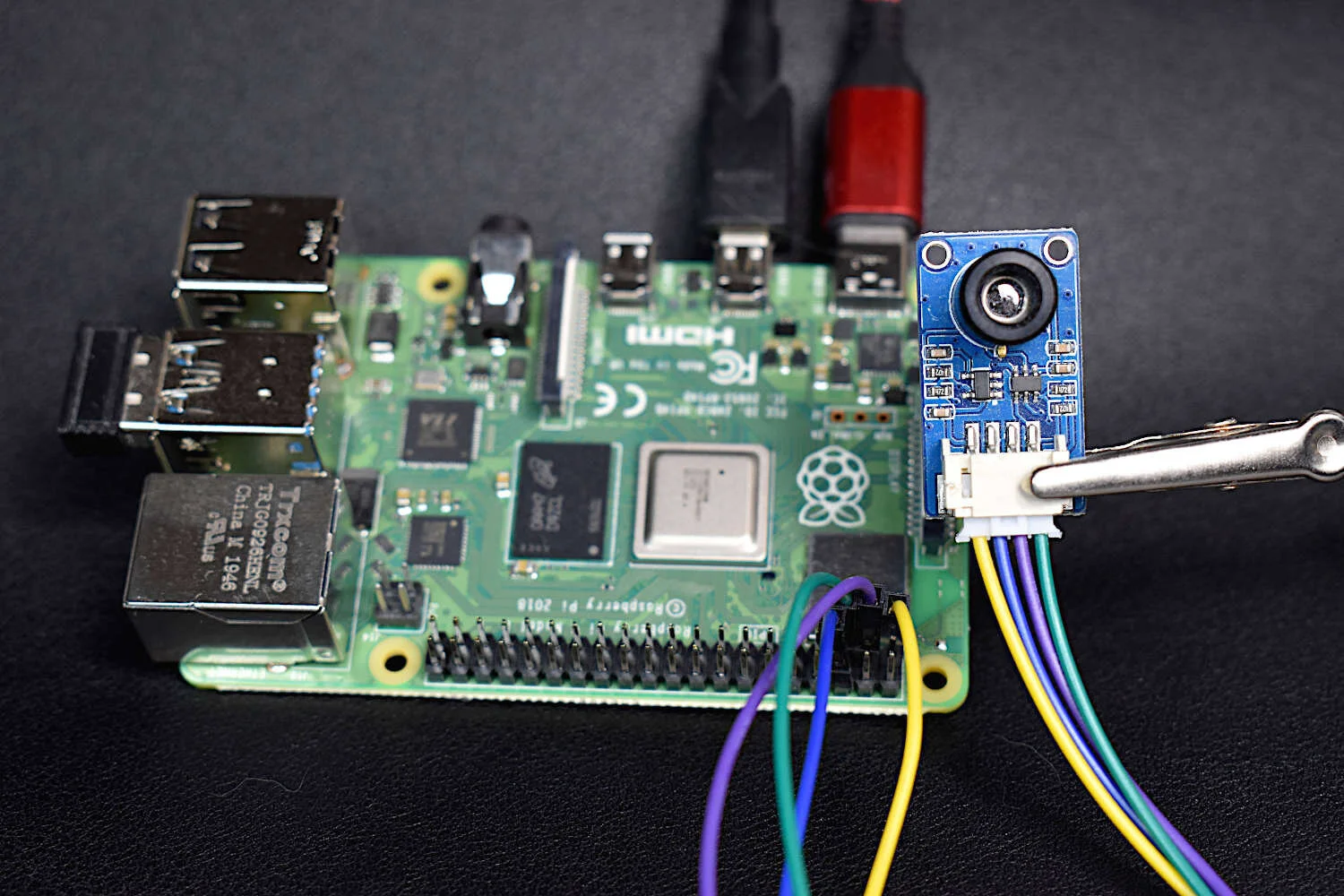
Thermal cameras are similar to standard cameras in that they use light to record images. The most significant distinction is that thermal cameras detect and filter light such that only the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum is recorded, not the visible region [read more about infrared cameras here]. Shortly after the discovery of the relationship between radiation and the heat given off by black bodies, infrared detectors were patented as a way to predict temperature via non-contact instrumentation. In recent decades, as integrated circuits shrink in size, infrared detectors have become commonplace in applications of non-destructive testing, medical device technology, and motion detection of heated bodies. The sensor used here is the MLX90640 [datasheet], which is a 768 pixel (24x32) thermal camera. It uses an array of infrared detectors (and likely filters) to detect the radiation given off by objects. Along with a Raspberry Pi computer, the MLX90640 will be used to map and record fairly high-resolution temeperature maps. Using Python, we will be able to push the RPI to its limits by interpolating the MLX90640 to create a 3 frame-per-second (fps) thermal camera at 240x320 pixel resolution.
Read MoreThis is a quick and fun tutorial on how to create an inexpensive laser pointer cat toy using DIY parts either found around the maker space or bought for other projects. It is an inexpensive and fun project that almost any maker or engineer could put together in a matter of minutes. It uses a cheap laser that can be found in many electronics kits (I’m using a red, 650 nm), a small button, and a 3.7V LiPo battery.
Read MoreHow to use a soft, circular-membrane potentiometer with an Arduino board. Potentiometers function by altering the voltage of a system by mechanically changing the resistance associated with a voltage divider. In a traditional potentiometer (think of turning a volume knob), we are physically changing the voltage of a system. In the case of a soft potentiometer (where the name SoftPot comes from), we are altering the resistance of the voltage divider by physically depressing the potentiometer, thereby changing the resistance at a contact point. The working principle is exactly the same, but in the SoftPot’s case, we are pressing, and for a knob we are rotating.
Read MoreIn this tutorial I will cover one of the newest microcontroller interface languages, Python, and demonstrate Adafruit's powerful Trinket M0 microcontroller and its capabilities using Python as its programming language. Much of what is outlined below can be seen on Adafruit's website [UART communication, Trinket info, CircuitPython Basics].
Read More